6 Tree coordinates
Tree coordinates have to be reported as polar coordinates in relation to the plot centre.
On behalf of the polar coordinate system each point on a plane is determined by
- the angle (azimuth) from magnetic North (as reference direction)
- and the distance (m) from the plot centre (as reference point)
How to calibrate the azimuth (gon):
a) The measurement point of each tree is located at 1,30m height (breast height), see pic 2.
b) Measure the angle (in gon) between tree and magnetic north (clockwise)
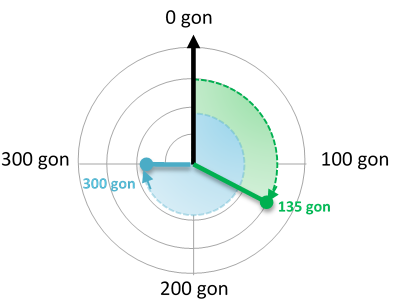
Pic 1: Magnetic north is the reference direction (0 gon) and the angle increases clockwise
c) Magnetic declination will not be considered to keep it simple.
How to calibrate the distance (m):
a) The measurement point of the tree is located at 1,30m height (breast height), see pic 2.
b) The point is located at the edge of the tree (not in front), in order the measure the distance to the tree centre. Alternatively, you can measure the distance to the tree front and add 1/2 DBH.
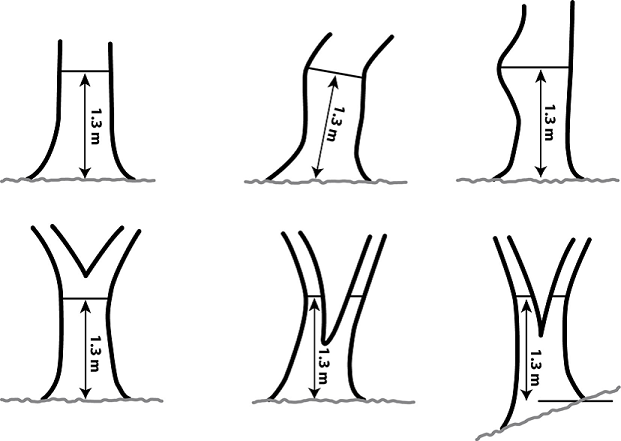
Pic 2: Where to measure dbh on trees with different form
How to correct the distance at slopes:
Polar coordinates are considered to be on a plane. Thus, if the site is located on a slope, it is required to convert the slope parallel distance into horizontal distance. This can be done by a simple formula: h = s * cos(α)
The picture below illustrates all relevant variables: plot centre (A), tree (B), slope parallel distance (s), slope angle (α), horizontal distance (h), elevation difference (e)
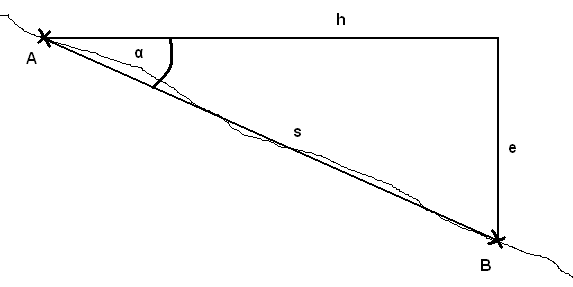
Note: It is important that distance (s) and slope (α) are measured in the same direction!